Breastfeeding is an essential aspect of child development, providing numerous benefits for both the mother and the baby. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the importance of breastfeeding and its positive impacts on the health, immunity, and emotional bonding of infants. From enhanced brain development to reduced risk of infections and chronic diseases, breastfeeding not only nourishes babies but also supports their long-term well-being. Additionally, we will address common misconceptions and offer practical tips for successful breastfeeding, making this overview an essential read for expecting or new mothers.
Benefits of Breastfeeding
Nutritional Benefits
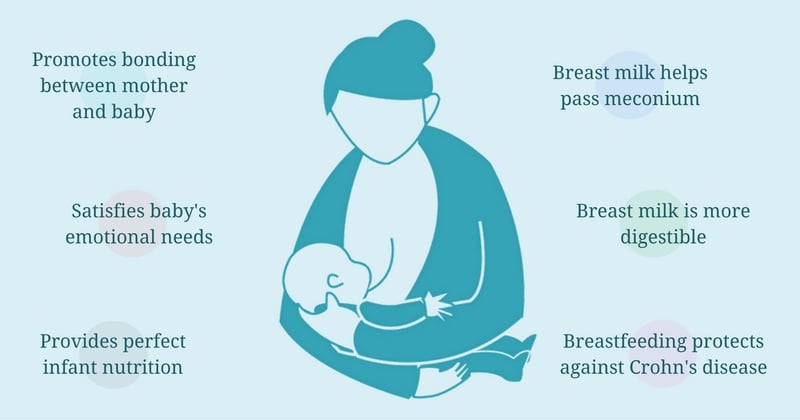
Breast milk is often referred to as “liquid gold” because it provides the perfect balance of nutrients for your baby’s growth and development. It contains all the essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that your baby needs in the first six months of life. Breast milk is easy to digest, which means that your baby can absorb all the nutrients efficiently.
Immune System Boost
Breast milk is packed with antibodies, immune cells, and enzymes that help protect your baby from various illnesses and infections. These antibodies are specifically tailored to target the pathogens that you and your baby are exposed to, providing a personalized immune defense. Breastfeeding has been shown to reduce the risk of ear infections, respiratory infections, gastrointestinal infections, and even some chronic diseases.
Brain Development
Breast milk contains high levels of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), which are crucial for the development of your baby’s brain and nervous system. Studies have shown that breastfed babies tend to have higher IQ scores and better cognitive development compared to babies who are formula-fed.
Allergy and Asthma Prevention
Breastfeeding has been linked to a reduced risk of allergies and asthma later in life. Breast milk contains proteins that help regulate your baby’s immune response and reduce the likelihood of developing allergies and asthma. The protection provided by breastfeeding is especially significant if you or your partner have a history of allergies.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
Breastfeeding has long-term health benefits for both you and your baby. For your baby, breastfeeding reduces the risk of developing chronic conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer later in life. As for you, breastfeeding has been associated with a lower risk of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Physical Benefits for Mothers
Postpartum Weight Loss
Breastfeeding can aid in postpartum weight loss. When you breastfeed, your body burns extra calories to produce milk, which can help you shed those extra pounds gained during pregnancy. It’s important to note that breastfeeding alone is not a guarantee of weight loss, as other factors like diet and exercise play a role too.
Reduced Risk of Breast Cancer
Breastfeeding has been shown to reduce the risk of breast cancer in mothers. The longer you breastfeed, the greater the protective effect. Breastfeeding stimulates the breasts, leading to a delay in the return of menstrual periods and a decrease in the levels of estrogen, which can help reduce the risk of breast cancer.
Lowered Risk of Ovarian Cancer
Studies have found that breastfeeding lowers the risk of ovarian cancer. The relationship between breastfeeding and ovarian cancer is complex, but the hormonal changes that occur during breastfeeding are believed to play a role in reducing the risk. The longer you breastfeed, the greater the protective effect.
Lowered Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Breastfeeding has been linked to a decreased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in mothers. Hormones released during breastfeeding help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the likelihood of developing diabetes later in life.
Reduced Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases
Breastfeeding has cardiovascular benefits for mothers. It has been associated with a lower risk of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and heart disease. The exact mechanisms are not fully understood, but it is believed that breastfeeding helps to regulate lipid metabolism and improve cardiovascular health.


Emotional Benefits for Mothers
Bonding with the Baby
Breastfeeding provides a unique opportunity for mothers to bond with their babies. The physical closeness and skin-to-skin contact involved in breastfeeding promote feelings of love, affection, and attachment. This bond can contribute to a strong emotional connection between you and your baby, fostering a sense of security and trust.
Release of Oxytocin
Oxytocin, often called the “love hormone,” is released during breastfeeding. It helps promote feelings of relaxation, calmness, and happiness. The release of oxytocin not only strengthens the bond between you and your baby but also provides a natural stress relief for you as a mother.
Reduced Risk of Postpartum Depression
Breastfeeding has been linked to a reduced risk of postpartum depression. The release of oxytocin during breastfeeding helps regulate mood and promotes a sense of well-being. Additionally, the close physical contact and emotional connection established during breastfeeding can provide a support system for mothers, reducing the feelings of isolation and loneliness often associated with postpartum depression.
Maternal Satisfaction
Breastfeeding offers a sense of accomplishment and fulfillment for many mothers. Knowing that you are providing your baby with the best possible nutrition and immune protection can boost your self-esteem and confidence as a mother. The emotional and physical benefits of breastfeeding can contribute to overall maternal satisfaction and a positive mothering experience.
Breastfeeding and Infant Health
Decreased Risk of SIDS
Breastfeeding has been associated with a decreased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). The exact reasons are still not fully understood, but breastfeeding promotes healthier sleep patterns and reduces the occurrence of respiratory infections, both of which are believed to contribute to the reduction in SIDS risk.
Lowered Risk of Respiratory Infections
Breastfeeding provides your baby with antibodies and immune cells that help fight respiratory infections. It has been found to reduce the risk of respiratory illnesses such as pneumonia, bronchiolitis, and even the common cold. The protective effect of breastfeeding against respiratory infections is particularly important in the first year of your baby’s life when their immune system is still developing.
Protection Against Childhood Obesity
Breastfeeding has been shown to decrease the risk of childhood obesity. Breast milk helps regulate your baby’s appetite and supports healthy growth. Breastfed babies have been found to have a better ability to self-regulate their food intake, reducing the likelihood of overeating and excessive weight gain.
Enhanced Cognitive Development
Breast milk contains essential nutrients and fatty acids that support optimal brain development. Numerous studies have shown that breastfed babies tend to have higher cognitive scores and improved intellectual development compared to formula-fed babies. The positive impact of breastfeeding on cognitive development can have long-lasting effects on your baby’s learning abilities and academic performance.
Reduced Risk of Ear Infections
Breastfeeding has been associated with a reduced risk of ear infections, also known as otitis media. Breast milk contains antibodies and other immune factors that help prevent the growth of bacteria and viruses in the middle ear. This reduces the susceptibility to ear infections, which can be painful and may lead to hearing loss if left untreated.


The Role of Breast Milk
Perfectly Balanced Nutrition
Breast milk is uniquely tailored to meet your baby’s nutritional needs. It contains the perfect balance of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals necessary for optimal growth and development. The composition of breast milk changes as your baby grows, adapting to their changing nutritional requirements.
Colostrum: Nature’s First Vaccine
Colostrum is the thick, yellowish milk produced in the first few days after birth. It is often referred to as “liquid gold” due to its rich nutrient content and high concentration of antibodies. Colostrum acts as your baby’s first vaccine, providing them with essential immune factors and helping to establish a healthy gut flora.
Digestive System Development
Breast milk helps support the development of your baby’s digestive system. It contains various enzymes and growth factors that promote the maturation of the intestines and improve the absorption of nutrients. Breastfed babies often experience less gastrointestinal distress, such as constipation or diarrhea.
Antibacterial and Antiviral Properties
Breast milk contains antibodies and other components that provide protection against a wide range of bacteria and viruses. It has antibacterial and antiviral properties that help prevent infections, especially in the gastrointestinal and respiratory systems. Breastfeeding helps to strengthen your baby’s immune system and provides them with active defense against harmful pathogens.
Passive Immunity Transfer
Breast milk transfers passive immunity to your baby, providing them with antibodies that you have developed throughout your life. These antibodies help protect your baby from the illnesses and infections that you have encountered. This passive transfer of immunity is particularly important during the first months of life when your baby’s own immune system is still developing.
Breastfeeding Challenges
Latching Difficulties
Latching difficulties can be a common challenge in breastfeeding. It is important to ensure that your baby is properly positioned and latched onto your breast to establish a good milk transfer. Seek support from a lactation consultant or a healthcare professional if you are experiencing difficulties with latching, as they can provide guidance and assistance.
Low Milk Supply
Some mothers may experience concerns about having a low milk supply. It’s important to remember that breastfeeding is a supply and demand process. The more you breastfeed or express milk, the more milk your body will produce. If you are concerned about your milk supply, consult with a lactation consultant who can provide guidance on increasing milk production and evaluate your breastfeeding technique.
Sore Nipples and Breast Engorgement
Sore nipples and breast engorgement can occur in the early stages of breastfeeding. This is often temporary and can be managed with proper positioning and latching techniques, as well as using warm compresses or cold packs to alleviate discomfort. If you are experiencing persistent soreness or engorgement, seek advice from a lactation consultant or healthcare professional.
Breast Infections: Mastitis
Mastitis is a breast infection that can occur while breastfeeding. It is usually caused by bacteria entering the breast through a cracked or sore nipple. Symptoms include breast pain, redness, and flu-like symptoms such as fever and chills. Prompt treatment with antibiotics, rest, and adequate milk removal can help resolve mastitis. Consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect you have mastitis.
Breastfeeding in Public
Breastfeeding in public can be a challenge for some mothers due to societal norms and lack of support. It’s important to remember that breastfeeding is a natural and necessary activity to nourish your baby. Many countries have laws that protect a mother’s right to breastfeed in public, and there are initiatives promoting breastfeeding-friendly spaces. Seek support from breastfeeding support groups or organizations to help navigate breastfeeding in public.


Breastfeeding and Society
Public Health and Economic Benefits
Breastfeeding has significant public health and economic benefits. It is a cost-effective way to improve infant health and reduce the burden on healthcare systems. Breastfed babies have lower healthcare costs, as they are less likely to suffer from various illnesses and chronic diseases. Breastfeeding also helps reduce the costs associated with formula feeding, such as purchasing formula and medical expenses for formula-fed infants.
Breastfeeding Policies and Legislation
Many countries have implemented policies and legislation to support breastfeeding. These policies include provisions for paid maternity leave, breastfeeding breaks at work, and protection against discrimination for breastfeeding mothers. Implementing and enforcing breastfeeding-friendly policies helps create a supportive environment for mothers to breastfeed and promotes the health and well-being of both babies and mothers.
Breastfeeding Support and Education
Breastfeeding support and education are essential for successful breastfeeding. Many healthcare organizations, community centers, and support groups offer breastfeeding education classes and lactation support services. These resources provide information on breastfeeding techniques, addressing breastfeeding challenges, and empowering mothers with the knowledge and skills necessary for a positive breastfeeding experience.
Breastfeeding-Friendly Workplaces
Breastfeeding-friendly workplaces have policies and facilities in place to support employees who are breastfeeding. These may include designated breastfeeding rooms, flexible work schedules, and paid breaks for expressing milk. Breastfeeding-friendly workplaces help mothers to continue breastfeeding once they return to work, supporting their commitment to providing breast milk to their babies.
Breastfeeding Peer Support Programs
Breastfeeding peer support programs connect mothers with experienced breastfeeding mothers who can provide practical advice and emotional support. These programs help address common breastfeeding challenges and provide a sense of community and reassurance. Peer support programs can be a valuable resource for new mothers as they navigate their breastfeeding journey.
Breastfeeding and Maternal Health
Postpartum Recovery
Breastfeeding can aid in postpartum recovery. The release of oxytocin during breastfeeding helps the uterus contract, reducing postpartum bleeding and promoting faster healing. Additionally, breastfeeding promotes a quicker return to pre-pregnancy weight and encourages the body to return to its pre-pregnancy state.
Delayed Return of Fertility
Breastfeeding can delay the return of fertility in some women. This is because breastfeeding can suppress the release of reproductive hormones that are necessary for ovulation and menstruation. The intensity, frequency, and duration of breastfeeding can affect its contraceptive effect, and it is important to use additional contraception if you do not wish to become pregnant.
Reduced Risk of Anemia
Breastfeeding is associated with a reduced risk of anemia in mothers. This is because breastfeeding delays the return of menstruation, reducing the loss of iron through menstrual blood. Additionally, breastfeeding stimulates the release of prolactin, which helps increase the maternal blood volume and supports iron absorption.
Providing Natural Birth Control
Breastfeeding can provide a natural method of birth control known as the Lactational Amenorrhea Method (LAM). LAM is based on the hormonally induced infertility that breastfeeding can provide. It is most effective when specific criteria are met, including exclusive breastfeeding, breastfeeding on demand day and night, and the absence of menstruation.
Lowered Risk of Osteoporosis
Breastfeeding has been associated with a decreased risk of osteoporosis in mothers. Pregnancy and breastfeeding require increased calcium intake to support the growth of your baby and the production of breast milk. While breastfeeding, your body becomes more efficient at absorbing and utilizing calcium, which helps preserve bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis later in life.


Breastfeeding Techniques
Positioning the Baby
Proper positioning is essential for successful breastfeeding. The “laid-back” position, also known as biological nurturing, allows your baby to naturally find their way to the breast. This position promotes good latch and milk transfer, reduces the strain on your back and arms, and encourages a comfortable breastfeeding experience for both you and your baby.
Achieving a Good Latch
A good latch is crucial for effective breastfeeding. It ensures that your baby is properly attached to the breast and able to extract milk efficiently. Signs of a good latch include your baby’s mouth covering a large portion of the areola, their lips turned outwards, and the absence of pain or discomfort during feeding. Seeking assistance from a lactation consultant can help you achieve and maintain a good latch.
Nursing on Demand
Breastfeeding on demand means letting your baby feed whenever they show hunger cues, rather than following a strict schedule. This approach allows for responsive feeding, ensuring that your baby gets the right amount of milk and meets their nutritional needs. Nursing on demand also helps establish a good milk supply and promotes a close bond between you and your baby.
Feeding on a Schedule
Some mothers choose to feed their babies on a schedule, rather than on demand. Feeding on a schedule can provide structure and predictability, especially for busy mothers. However, it is important to ensure that your baby is still able to feed whenever they show hunger cues, as their nutritional needs may vary from day to day. Balancing a schedule with responsive feeding is key to successful breastfeeding.
Breastfeeding with Pump and Bottles
Breastfeeding with a pump and bottles can be useful for mothers who need to be separated from their babies or want to provide expressed breast milk. It is important to choose a breast pump that suits your needs and learn proper pumping techniques. Introducing bottles can be done gradually to ensure that your baby continues to breastfeed effectively and maintains a good latch.
Breastfeeding Duration and Weaning
Exclusive Breastfeeding
Exclusive breastfeeding means feeding your baby only breast milk, without the introduction of any other liquids or solid foods, except for vitamins, minerals, or medications as advised by a healthcare professional. Exclusive breastfeeding is recommended for the first six months of your baby’s life, as breast milk provides all the necessary nutrients and immune protection during this time.
Breastfeeding for at least 6 months
Breastfeeding is recommended for at least six months, along with the introduction of appropriate complementary foods. Breast milk continues to provide essential nutrients and immune factors that support your baby’s growth and development. The World Health Organization and various health organizations recommend continuing breastfeeding alongside solid foods for up to two years or beyond.
Continued Breastfeeding up to 2 years
Breastfeeding can be continued beyond the age of one year, as long as both you and your baby are comfortable and willing to continue. Breast milk continues to provide nutritional benefits and immune protection, while breastfeeding offers emotional comfort and support for your growing toddler. The decision to continue breastfeeding beyond two years is a personal one, based on the needs and preferences of both you and your child.
Introducing Solid Foods
Introducing solid foods to your baby’s diet is an important milestone in their development. Starting around six months of age, you can gradually introduce a variety of age-appropriate foods alongside breastfeeding. Breast milk remains an important part of your baby’s diet, providing essential nutrients and immune protection while they explore new flavors and textures.
Gradual Weaning Process
Weaning is the process of gradually reducing breastfeeding and transitioning your baby to a diet that consists primarily of solid foods and other sources of nutrition. Weaning can be a gradual process, taking into consideration your baby’s readiness for different foods and their individual needs. It is a unique journey for every mother and baby, and it is important to approach weaning with patience, support, and understanding.
In conclusion, breastfeeding offers numerous benefits for both you and your baby. From providing optimal nutrition and boosting the immune system to promoting bonding and reducing the risk of chronic diseases, breastfeeding sets the foundation for a healthier future. Overcoming challenges, seeking support, and finding a breastfeeding routine that works for you and your baby are key to a successful breastfeeding experience. Remember, every breastfeeding journey is unique, and what matters most is the well-being and happiness of both you and your little one.