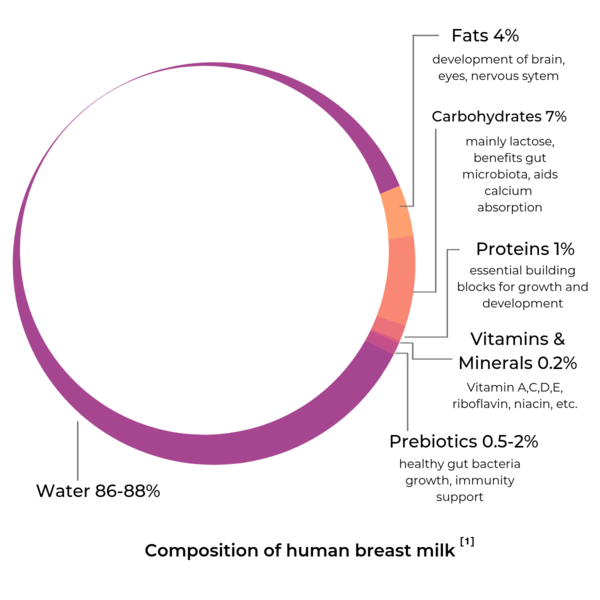
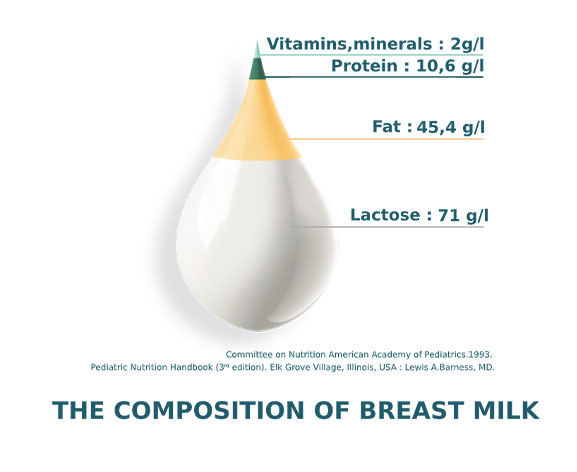
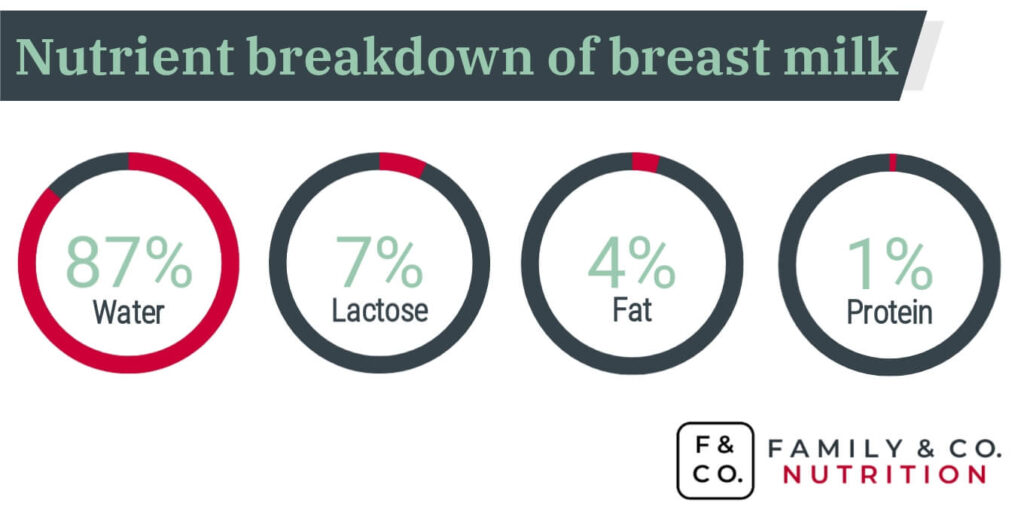
Did you know that breast milk contains a unique mix of nutrients that are specifically tailored to meet your baby’s needs? From proteins and fats to vitamins and minerals, breast milk provides all the essential nutrients your baby requires for healthy growth and development. In this article, we will explore the nutritional components of breast milk and how they contribute to your baby’s wellbeing. Discover the amazing benefits of breastfeeding and learn why breast milk is often referred to as the “gold standard” for infant nutrition. Breast milk is often referred to as “liquid gold” due to its unique and incredibly beneficial nutritional composition. It provides infants with all the necessary nutrients for healthy growth and development, ensuring that they receive the best start in life. Let’s explore the various components of breast milk and their importance in nourishing your baby.
Protein
Casein
One of the key proteins found in breast milk is casein. It is easily digestible and provides a balanced blend of essential amino acids that are crucial for your baby’s overall growth and development. Casein plays a significant role in bone development and aids in the absorption of essential minerals such as calcium and magnesium.
Whey
Whey protein is another vital component of breast milk. It is highly digestible and offers various health benefits for your little one. Whey protein contains important amino acids, including cysteine, which supports the production of the antioxidant glutathione, promoting a healthy immune system. It also helps in the absorption of iron and enhances cognitive development in infants.
Antibodies
Breast milk is rich in antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, which are crucial for boosting your baby’s immune system. These antibodies protect your little one from various infections and diseases, providing them with passive immunity in the initial months of life when their own immune system is still developing.
Carbohydrates
Lactose
Lactose is the primary carbohydrate present in breast milk. It is a source of readily available energy for your baby. Lactose also aids in the absorption of essential minerals like calcium and enhances the growth of beneficial probiotic bacteria in the gut, promoting overall digestive health.
Oligosaccharides
Breast milk contains a high concentration of oligosaccharides, which are complex carbohydrates that cannot be digested by your baby’s enzymes. While they may not be directly absorbed, they serve as prebiotics, promoting the growth of healthy bacteria in the gut. This helps in strengthening the immune system and protecting against harmful pathogens.


Fats
Fats in breast milk play a crucial role in providing energy and supporting your baby’s growth and development. The fats present in breast milk are classified into different categories:
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are the primary fats in breast milk. They provide a concentrated source of energy and support brain development. The fatty acids found in triglycerides are vital for the development of the nervous system and visual acuity.
Cholesterol
Despite its reputation, cholesterol is essential for infants’ growth and development. It plays a significant role in brain and nervous system development, as well as hormone production. Breast milk naturally contains the optimal amount of cholesterol needed for your baby’s health.
Fatty Acids
Breast milk provides a rich source of essential fatty acids, including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are crucial for your baby’s brain development and overall cognitive function. These fatty acids also support vision development and promote a healthy immune system.
Vitamins and Minerals
Breast milk contains a wide range of vitamins and minerals that are essential for your baby’s overall health and development. Let’s explore some of the key vitamins and minerals found in breast milk:
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is crucial for your baby’s immune function, vision development, and cell growth. Breast milk provides an optimal amount of vitamin A, ensuring your little one has a healthy start.
Vitamin D
Breast milk contains varying amounts of vitamin D depending on the mother’s own levels. This vitamin plays a critical role in bone health and calcium absorption, supporting your baby’s growth and development.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects your baby’s cells from damage. It also supports immune function and aids in the formation of red blood cells.
Vitamin K
Breast milk is a natural source of vitamin K, which is essential for blood clotting and preventing bleeding disorders in newborns.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C plays a vital role in boosting your baby’s immune system and promoting the absorption of iron from breast milk. It also supports the formation of collagen, which is necessary for healthy skin, bones, and connective tissues.
Thiamin
Thiamin, also known as vitamin B1, is essential for your baby’s nervous system development and carbohydrate metabolism.
Riboflavin
Riboflavin, or vitamin B2, is crucial for energy production and cellular growth. It also supports healthy vision and skin development.
Niacin
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, aids in energy production, DNA repair, and supports normal brain function.
Pantothenic Acid
Pantothenic acid, or vitamin B5, is involved in energy metabolism and the production of hormones and cholesterol.
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 plays a vital role in brain development, the production of neurotransmitters, and the metabolism of proteins.
Folate
Folate, also known as vitamin B9, is essential for proper cell growth and the formation of DNA. It is particularly crucial during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is necessary for your baby’s brain development and the production of red blood cells. Breast milk provides a reliable source of this important nutrient.
Minerals
Breast milk contains an array of minerals, including calcium, phosphorus, iron, zinc, and many others. These minerals play essential roles in bone development, oxygen transport, and overall growth.
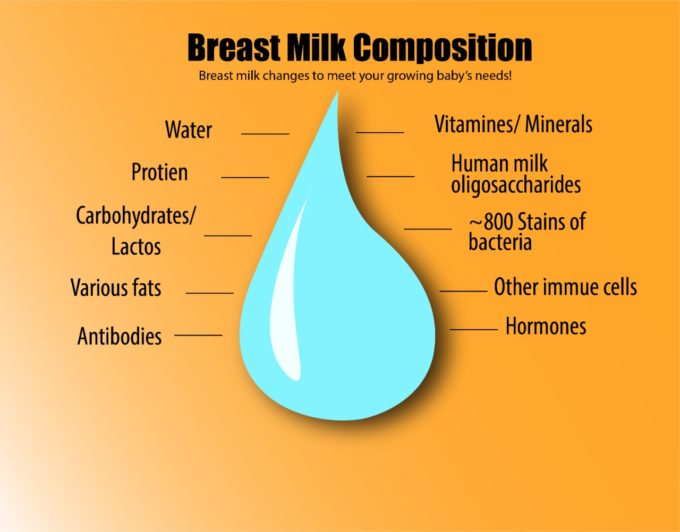

Hormones
Breast milk contains various hormones that help regulate your baby’s bodily functions and overall well-being. Let’s explore some of the hormones found in breast milk:
Leptin
Leptin plays a role in regulating appetite and promoting healthy weight gain in infants. It helps your baby feel satiated and contributes to the development of a healthy metabolism.
Insulin
Insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels, ensuring your baby’s body can properly use the carbohydrates from breast milk.
Cortisol
Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, is present in breast milk. It helps your baby’s body respond to stress and regulates their sleep-wake cycle.
Epidermal Growth Factor
Epidermal growth factor promotes healthy cell growth and repair. It plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of your baby’s digestive system.
Enzymes and Digestive Factors
Breast milk contains various enzymes and digestive factors that aid in the digestion and absorption of nutrients. Let’s explore some of these components:
Amylase
Amylase is an enzyme that helps break down complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars for easier absorption and digestion.
Lipase
Lipase is an enzyme that breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol, making them more accessible for your baby’s body to absorb.
Lactoferrin
Lactoferrin is a multifunctional protein that promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut and supports the immune system.
Lysozyme
Lysozyme is another enzyme found in breast milk that helps protect your baby against harmful bacteria and viruses.
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide
Gastric inhibitory peptide helps regulate the release of digestive juices in your baby’s stomach, ensuring efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients.
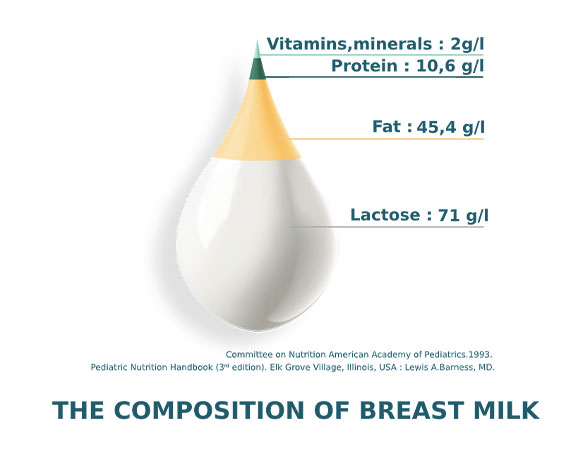

Immunoglobulins
Breast milk is rich in various types of immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, that provide your baby with passive immunity. Let’s take a closer look:
IgA
IgA is the predominant antibody in breast milk. It helps protect your baby’s mucosal surfaces, particularly in the digestive and respiratory tracts, providing defense against infections.
IgG
IgG is another important antibody passed through breast milk. It provides systemic immunity and protects against a wide range of viruses and bacteria.
IgM
IgM antibodies are present in smaller amounts but offer protection against specific pathogens, strengthening your baby’s immune system.
IgD
IgD antibodies play a role in regulating immune responses and promoting the production of other antibodies.
IgE
IgE antibodies are associated with allergic reactions but also provide protection against certain parasites.
Nucleotides
Breast milk contains nucleotides, which are the building blocks of DNA and RNA. These nucleotides play a role in promoting optimal growth, development, and immune function in your baby.

Hormones and Growth Factors
In addition to the hormones mentioned earlier, breast milk also contains several growth factors that support your baby’s overall development. Let’s explore some of them:
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone promotes overall growth and development, supporting your baby’s bone and muscle growth.
Prolactin
Prolactin is the hormone responsible for milk production. It also promotes bonding between mother and baby.
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone helps regulate your baby’s thyroid gland, which plays a crucial role in metabolism and overall growth.
Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, play a role in regulating metabolism, immune function, and stress response.
Bioactive Factors
Breast milk contains various bioactive factors that provide additional health benefits to your baby. Let’s explore some of them:
Lactoferrin
Lactoferrin, mentioned earlier, not only aids in digestion but also has antimicrobial properties and supports the immune system.
Lysozyme
Lysozyme, also mentioned earlier, helps protect your baby against harmful bacteria and viruses.
Epidermal Growth Factor
Epidermal growth factor supports the development and repair of your baby’s skin, gastrointestinal tract, and other epithelial tissues.
Bifidus Factor
Bifidus factor promotes the growth of beneficial bifidobacteria in your baby’s gut, helping to maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
Breast milk is an incredible and complex fluid that provides all the essential nutrients, antibodies, hormones, and bioactive factors your baby needs for optimal growth and development. Its composition is tailored to meet your baby’s specific nutritional requirements, making it the best nourishment you can provide.